EventBridge (opens new window) is one of the powerful tools in the AWS toolbox when you move towards loosely coupled / event-driven architectures.
In this blog post, I would like to explain by example one of my use cases of EventBridge (opens new window) using API Destinations (opens new window).
# What is EventBridge?
EventBridge (opens new window) is a serverless event bus that enables you to build event-driven applications at scale using events generated from your applications.
# How it works?
Evnebridge connects applications using events, You can fire an event from one of your applications and define filtering rules to route them to specific targets. Those targets can be AWS Services in the same AWS account, another AWS account, or API Destinations (opens new window) via HTTP.
# What are API Destinations?
API Destinations are a form of 3rd party targets(SaaS applications)that can be invoked by event bridge events using REST API calls. API Destinations (opens new window) supports basic, OAuth, and API Key authorization. There are many API destination partners listed here, but you can also use this feature with any 3rd party that has a REST API.
# A working examples
I usually use API Destinations when I want to decouple an asynchronous call from my logic, and when that call invokes a 3rd party REST API.
Let us assume we are implementing the following scenario
GIVEN A User add their details to the website
AND User data is valid
WHEN User data is saved successfully
THEN a UserCreated event is broadcasted
AND an Email is sent to the user
AND an identify fraud check is triggered
So we are building a POST endpoint that accepts user adds a user to the database, and then sends a thank you email to the user after.
We are using SendGrid (opens new window) as an email provider to send the thank you email utilizing their API.
There are multiple ways to achieve that in the cloud to do this asynchronous call but I prefer API Destinations (opens new window) because it is a low code approach. I won't have to write the logic to connect to SendGrid (opens new window) API, manage the retries, etc. I can just send the event and create a rule to call.
# Architecture
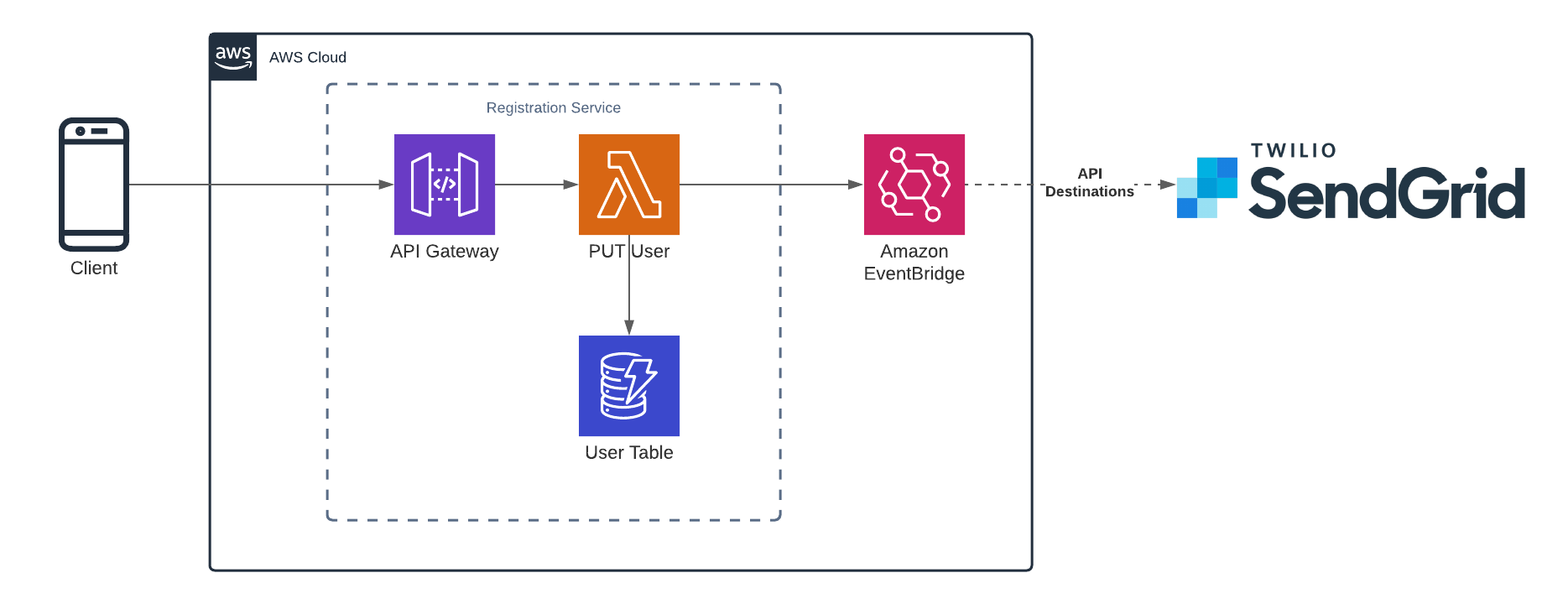
The full code explained below can be found in Github (opens new window)
In this example We, we will use the default events bus, and we will use AWS SAM (opens new window) to build our project
# Implementation Steps:
- Create our lambda functions cloudformation resource
putUserFunction:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
Handler: src/handlers/put-user.putUserHandler
Runtime: nodejs14.x
MemorySize: 128
Timeout: 100
Description: A simple example includes a HTTP post method to add one user to a DynamoDB table, and send an event to eventbridge
Policies:
- DynamoDBCrudPolicy:
TableName: !Ref UserTable
Environment:
Variables:
USER_TABLE: !Ref UserTable
Events:
Api:
Type: Api
Properties:
Path: /user
Method: POST
- Add the Arn of the default EventBridge bus, and the SendGrid API so we refer to it in different parts of the template
CentralBusArn:
Description: Arn for central event bus
Type: String
Default: "arn:aws:events:eu-west-1:0000000000:event-bus/default"
SendgridApiKey:
Description: SendGrid API Key
Type: String
Default: "Bearer SendGridSecretApiKey"
- Now lets Write the logic that adds the user to the dynamoDB table
const dynamodb = require('aws-sdk/clients/dynamodb');
const docClient = new dynamodb.DocumentClient();
const { uuid } = require('uuidv4');
const tableName = process.env.USER_TABLE;
exports.putUserHandler = async (event) => {
const body = JSON.parse(event.body)
const userData = {id: uuid(), name: body.name, email: body.email}
var dynamoDBparams = {
TableName: tableName,
Item: userData
};
// Store the user data in the dynamoDB table
const result = await docClient.put(dynamoDBparams).promise();
const response = {
statusCode: 200,
body: JSON.stringify(body)
};
return response;
}
- Next we give permission for the lambda to Put Events in EventBridge
Policies:
- DynamoDBCrudPolicy:
TableName: !Ref UserTable
- Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- events:PutEvents
Resource: "*"
- Next Step lets create our SendGrid destination
SendgridApiDestination:
Type: AWS::Events::ApiDestination
Properties:
ConnectionArn:
Fn::GetAtt: [SendgridConnection, Arn]
InvocationEndpoint: 'https://api.sendgrid.com/v3/mail/send'
HttpMethod: POST
InvocationRateLimitPerSecond: 300
- Now lets create the connection to Sendgrid and refer to the API Key we added previously
SendgridConnection:
Type: AWS::Events::Connection
Properties:
AuthorizationType: API_KEY
Description: 'Sendgrid API Credentials'
AuthParameters:
ApiKeyAuthParameters:
ApiKeyName: Authorization
ApiKeyValue: !Ref SendgridApiKey
- Now we need to create the filtering rule for the destinations API with the payload we want to send to SendGrid API containing data from the UserCreated event
ApiDestinationDeliveryRule:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: !Ref CentralBusArn
EventPattern:
source:
- "com.users"
detail-type:
- "UserCreated"
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Arn: !GetAtt SendgridApiDestination.Arn
Id: SendgridTarget
RoleArn: !GetAtt SendgridTargetRole.Arn
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
name: $.detail.name
email: $.detail.email
InputTemplate: >
{
"personalizations": [
{
"to": [
{
"email": "hello@example.com"
}
]
}
],
"from": {
"email": "hello@example.com"
},
"subject": "<name>, Registration Comlete",
"content": [
{
"type": "text/plain",
"value": "Hey <name>, Using Eventbridge Destinations is Fun and easy to do ;)"
}
]
}
- Next we create the IAM ole to allow eventbridge to Invoke an API Destination
SendgridTargetRole:
Type: 'AWS::IAM::Role'
Properties:
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: "2012-10-17"
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service:
- events.amazonaws.com
Action:
- 'sts:AssumeRole'
Policies:
- PolicyName: Amazon_EventBridge_Invoke_Sendgrid_API_Destination
PolicyDocument:
Version: "2012-10-17"
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action: events:InvokeApiDestination
Resource: !GetAtt SendgridApiDestination.Arn
- Last thing we modify our code to send the actual event to EventBridge
const eventBridgeParam = {
Entries: [
{
// Event envelope fields
Source: 'com.users',
EventBusName: 'default',
DetailType: 'UserCreated',
Time: new Date(),
// Main event body
Detail: JSON.stringify(userData)
},
]
}
await eventbridge.putEvents(eventBridgeParam).promise()
- Now to test, all we need to do is to invoke the lambda function by sending a POST request to the API URL
curl -X POST \
https://bi82zcrsa4.execute-api.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/Prod/user \
-H 'cache-control: no-cache' \
-H 'content-type: application/json' \
-d '{
"name" : "Me2resh",
"email" : "me2resh@example.com"
}'
You should receive the email containing the name of the user from SendGrid
This was one of my favourite use cases of Eventbridge, the full code for the example is here https://github.com/me2resh/eventbridge-api-destinations-example (opens new window). I hope you learned a new way to communicate with an external API through events without writing the code, and only through configuration.